Breathing city air leads to cancer, heart attacks, strokes and other diseases of today
What is the body's greatest need? What do you think?
This article was translated from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, which has been studying for 50 years how polluted air affects our environment and human health. The Institute publishes many studies on how air pollution affects health and the population groups that are most affected. Below you can read very important information that concerns people living in cities, where the greatest air pollution is present.
Air pollution is a known environmental health hazard. We know what we're looking at when a brown haze descends over a city, exhaust fumes billow across a busy highway, or a plume rises from a chimney. Some air pollutants are not visible, but their pungent smell warns you. It is a great threat to our health and the health of our loved ones. Air pollution, in all its forms, is responsible for more than 6.5 million deaths every year in the world, a number that has increased over the past two decades.
What is air pollution?
Air pollution is a mixture of dangerous substances that comes from bad decisions people make. Emissions from vehicles, fuel oil and natural gas for heating homes, by-products of electricity production and production, especially coal-fired power plants, and fumes from chemical production are the primary sources of human-caused air pollution.
Air pollution caused by traffic (TRAP), a mixture of gases and particles, has most of the elements of human-caused air pollution: ground-level ozone, various forms of carbon, nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, volatile organic compounds, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and fine particles.
Ozone, an atmospheric gas, is often called smog when it is at ground level. It is formed when pollutants emitted by cars, power plants, industrial boilers, refineries and other sources react chemically in the presence of sunlight.
Harmful gases, which include carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulfur oxides (SOx), are components of motor vehicle emissions and by-products of industrial processes.
Particles (PM) consist of chemicals such as sulfates, nitrates, carbon or mineral dust. Emissions from vehicles and industry resulting from the burning of fossil fuels, cigarette smoke and the burning of organic matter, such as forest fires, contain particulate matter.
A subset of PM, fine particles (PM 2.5) is 30 times thinner than a human hair. It can be inhaled deep into the lung tissue and cause serious health problems. PM 2.5 is responsible for most health effects due to air pollution in the US.
Volatile organic compounds (VOC) evaporate at or near room temperature - hence the name volatile. They are called organic because they contain carbon. VOCs are released by paints, cleaning products, pesticides, some furniture, and even craft materials like glue. Gasoline and natural gas are the main sources of VOCs released during combustion.
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are organic compounds containing carbon and hydrogen. Of the more than 100 PAHs known to be widely distributed in the environment, 15 of them are listed in the Report on Carcinogens. In addition to combustion, many industrial processes, such as the production of iron, steel and rubber products, as well as the generation of electricity, also produce PAHs as a by-product. PAHs are also found in particulate matter.
What does NIEHS (National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences) do?
During its 50-year history, NIEHS has been a leader in air pollution research. The institute continues to fund and conduct research on how air pollution affects health and the population groups most affected.
How does air pollution affect our health?
When the National Air Quality Standards were established in 1970, air pollution was considered primarily a threat to the health of the respiratory system. In 1993, NIEHS researchers published a landmark study of six cities, which established a link between fine particles and mortality. Exposure to air pollution is linked to oxidative stress and inflammation in human cells, which can set the stage for chronic disease and cancer. In 2013, the International Agency for Research on Cancer of the World Health Organization (WHO) classified air pollution as carcinogenic to humans. Research on air pollution and its effects on health is constantly progressing. Public health concerns now include cancer, cardiovascular disease, respiratory disease, diabetes mellitus, obesity, and reproductive, neurological, and immune system disorders.
Malignant diseases (Cancer)
A large study of more than 57,000 women showed that those who live near major roads can increase the risk of breast cancer. A sister NIEHS study found that other airborne toxicants, particularly methylene chloride, which is used in aerosol products and paint removers, are also linked to increased risk of breast cancer. Occupational exposure to benzene, an industrial chemical and component of gasoline, can cause leukemia and is associated with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. A long-term study, 2000-2016, revealed a connection between the incidence of lung cancer and increased reliance on coal for energy production.
Cardiovascular diseases
Fine particles can disrupt the function of blood vessels and accelerate calcification in the arteries.
- NIEHS researchers have established links between short-term daily exposure to nitric oxide in postmenopausal women and an increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke.
- For some older Americans, TRAP exposure (Air pollution caused by traffic) can result lower levels of high-density lipoprotein, sometimes called good cholesterol, increasing their risk of cardiovascular disease.
- According to a report by the National Toxicology Program (NTP), exposure to TRAP also increases a pregnant woman's risk of dangerous changes in blood pressure, known as hypertensive disorders, which are a leading cause of preterm birth, low birth weight, and maternal and fetal distress. sickness and death.
Disease of the respiratory system
- Air pollution can affect lung development and is involved in development emphysema, asthma and other diseases of the respiratory system, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- PM(Particulate matter) and nitrogen oxide are associated with chronic bronchitis.
- In 2020, a major public health challenge was the combination of the COVID-19 pandemic and wildfires across the western U.S. Building on the well-established link between air pollution and respiratory infections, the study linked forest fire smoke with additional cases of COVID-19 i deaths.
Who is most affected by air pollution?
Air pollution affects everyone's health, but certain groups may be more affected. Almost 9 out of 10 people living in urban areas around the world are affected by air pollution, he says study.
You can check more about air quality in Croatia below: http://iszz.azo.hr/iskzl/
You can check more about air quality in the world below: https://www.iqair.com/world-air-quality-ranking
What are the consequences for children
The NIEHS-funded Children's Health Study at the University of Southern California is one of the largest studies of the long-term effects of air pollution on children's respiratory health. Among his findings:
- Higher levels of air pollution they increase short-term respiratory infections, which leads to more absences from school.
- Children who engage several outdoor sports and living in high ozone communities are more likely to develop asthma.
- Children who live near busy roads have an increased risk of asthma.
- Children with asthma who were exposed to high levels of air pollutants were more likely to develop symptoms of bronchitis.
- Living in communities with higher levels of pollution can cause lung damage
Older adults
Alzheimer's disease and related dementias represent a public health challenge for the aging population. NIEHS-funded University of Washington researchers have identified a link between air pollution and dementia. This well-conducted study adds significant evidence that fine particles in the ambient air increase the risk of dementia.
- Air pollution is associated with higher odds for the development of several neurological disorders, including Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and other dementias. Hospital admission data for 63 million older adults in the US, obtained over 17 years (2000-2016), were analyzed along with estimated PM(Particulate Matter) 2.5 concentrations by zip code to conduct the study.
- In the elderly, long-term exposure to TRAP (Air pollution caused by traffic) can significantly accelerate physical defects. The risk is more pronounced among racial minorities and people with lower incomes.
- PM 2.5 air pollution is also related with accelerated memory problems and Alzheimer's-like brain failure, which was observed in women aged 65 and older. Conversely, a multi-year study published in 2022 shows that improved air quality is linked with a lower risk of dementia in older women. The researchers also stated that this reduction in the risk of dementia was equivalent to reducing the age of the subjects by almost 2 1/2 years.
- Nutrients can prevent some harmful effects of air pollution. A 2020 study showed that omega-3 fatty acids, obtained by consuming certain fish (which we don't recommend, because fish is highly polluted with heavy metals, the replacement is whole flaxseed that you eat every day), can protect against chemicals in the air in older women.
Why improving air quality is important
The researchers analyzed indoor and outdoor air pollution data from all populated continents along with key pregnancy outcomes. Their findings show that efforts to reduce exposure to particulate chemicals could lead to to a significant reduction in the number of low birth weight and premature babies worldwide. Reducing air pollution would be particularly beneficial for children born in low- and middle-income countries.
- Among children in Southern California, reductions in environmental nitrogen dioxide and particulate chemicals have been linked with fewer cases of asthma.
- A study funded by the Institute found that several vitamins B6, B9, B12 can protect DNA from changes which can be attributed to air pollution. An excellent food supplement that contains enough B6, B9, B12 vitamins is Superfood plus.
- Bronchitis symptoms have decreased as pollution levels dropped in the Los Angeles region.
- Improving air quality can improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of dementia, according to studies which was supported in part by the NIH and the Alzheimer's Association.
- When fossil fuel power plants close down, nearby air pollution decreases. Study showed that the incidence of preterm births decreased within 5 kilometers of a decommissioned coal and oil plant site.
The conclusion is very simple, in order to reduce the probability of getting sick from the diseases mentioned in the studies, one should move away from the cities, practice a healthy lifestyle and clean the entire organism.
In addition, we suggest that you read what hypoxia (displacement of oxygen) can do to your body:
In 1931, the German scientist Otto Heinrich Warburg (1883-1970) received the Nobel Prize for finding the root cause of cancer. dr. Warburg discovered that cancer is the result of an anti-physiological lifestyle. With an anti-physiological way of eating (predominantly acidifying food) and physical inactivity, the body creates an acidic environment that is poorly supplied with oxygen.
Cellular acidity displaces oxygen, and lack of oxygen in cells creates an acidic environment.
dr. Warburg said: "Lack of oxygen and acidity are two sides of the same coin: if one has one, one has the other." If you have too high acidity, you will automatically lack oxygen in your body; if you lack oxygen, you will have an acidified organism. An acidic environment is an environment without oxygen. "If you deprive a healthy 35% cell of its oxygen, you can turn it into a cancer cell in just two days," claimed Dr. Warburg.
"All normal cells have an absolute need for oxygen, but tumor cells can live without it. It is a rule without exception".
Tumor tissues are acidic, while healthy tissues are alkaline
 In his work "Tumor metabolism", Dr. Warburg showed that all cancerous forms fulfill two basic conditions: blood acidity and hypoxia (lack of oxygen). He discovered that tumor cells are anaerobic (do not breathe oxygen) and cannot survive in the presence of high concentrations of oxygen.
In his work "Tumor metabolism", Dr. Warburg showed that all cancerous forms fulfill two basic conditions: blood acidity and hypoxia (lack of oxygen). He discovered that tumor cells are anaerobic (do not breathe oxygen) and cannot survive in the presence of high concentrations of oxygen.
Tumor cells can survive only with the help of glucose and in an environment without oxygen. Therefore, cancer is nothing but a defense mechanism that our cells use to survive in an acidic environment without the presence of oxygen. Healthy cells live in an alkaline environment full of oxygen, which enables their normal functioning. Tumor cells live in an acidic environment poor in oxygen. Acidity of the organism is the name for various conditions in which the relationship between acids and bases in the organism is disturbed, so the pH value of blood and urine is shifted towards an acidic reaction, that is, pH < 7.35. The opposite state of the acidity of the organism is the alkalinity of the organism, when the pH value of blood and urine is >7.45.
 The acidity of the body is suitable for the development of many diseases (low energy level, chronic fatigue, excessive mucus production, frequent colds and infections, nervousness, irritability, brittle nails, dry hair and skin, cyst formation, headaches, painful joints and arthritis, neuritis, muscle pains and spasms, gastritis, cancer, autoimmune diseases...), so in a healthy and balanced diet it is important to maintain a neutral reaction of the body. This is achieved by choosing the right foods, because the acid neutralizes the base and vice versa.
The acidity of the body is suitable for the development of many diseases (low energy level, chronic fatigue, excessive mucus production, frequent colds and infections, nervousness, irritability, brittle nails, dry hair and skin, cyst formation, headaches, painful joints and arthritis, neuritis, muscle pains and spasms, gastritis, cancer, autoimmune diseases...), so in a healthy and balanced diet it is important to maintain a neutral reaction of the body. This is achieved by choosing the right foods, because the acid neutralizes the base and vice versa.
A little reminder of chemistry lessons: The basicity and acidity of a substance are determined using the pH value (hydrogen ion concentration). In doing so, the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH) is measured, which give pH values greater than 7 and a basic reaction, or the concentration of hydrogen ions (H), which give pH values less than 7 and an acidic reaction. But what role do bases and acids play in the body? Do they give or take energy? The reaction in which bases are formed implies any chemical change in the body due to which its energy increases, and the urine becomes alkaline. A reaction in which acids are formed implies any chemical change due to which the body's energy decreases and the urine becomes acidic. All organs in the human body function normally only when the amounts of basic and acidic substances in the body are in the right balance.
For example but even slightly acidic blood can cause a number of problems, not only in the heart but also in the kidneys, lungs, and liver. All food after passing through the gastrointestinal tract first comes to the liver. This is why the burden on the liver is greater if waste acids are constantly circulating in the blood.
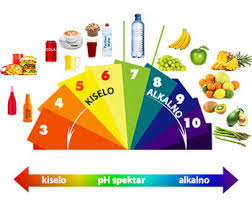 Here is a list that expresses the degree of acidity and alkalinity of certain types of food. The higher the number (blue), the more alkaline (basic) the food is. The smaller it is (red), the more acidic it is.
Here is a list that expresses the degree of acidity and alkalinity of certain types of food. The higher the number (blue), the more alkaline (basic) the food is. The smaller it is (red), the more acidic it is.
pH 9.0 – Lemon, watermelon
pH 8.5 – Melons, grapes, parsley, kiwi, pears, pineapple, raisins, umeboshi plums, vegetable and fruit juices, dried figs, dried dates, peppers, mango, papaya, raspberries, tangerines, onions.
pH 8.0 – Fresh dates and figs, sweet apples, apricots, bananas, carrots, celery, garlic, avocado, grapefruit, lettuce, nectarines, peaches, pumpkins, spinach, broccoli.
pH 7.5 – Sour apples, beets, cabbage, cauliflower, ginger, potatoes, strawberries, olives
pH 7.2-7.3 – Almonds, homemade cucumbers, artichokes, cherries, cucumbers, homemade honey, mushrooms, ripe and fresh olives, radishes, sesame seeds, tomatoes, olive oil, various spices, coconut and linseed oil.
pH 6.7-6.8 - Plums, prunes, coconut, and most of its products, pistachios, beans, pasteurized honey, pumpkin and sunflower seeds, vanilla...
pH 6.5 - Bread made from oats, rye, barley, rice, integral rice, corn bread, soy milk, soy cheese, almond and sesame oil, sunflower and grape oil.
pH 6.0 – Fish, cheese, ketchup, mayonnaise, fruit juices with sugar, cigarettes (from fresh tobacco), popcorn, pickles, goat's milk, mustard, molasses, cow's milk, turkey, shellfish, duck meat, casein (milk protein), refined grains ( such as corn flakes), fat, palm oil, sweetened yogurt, peanuts, cranberries, processed cheese.
pH 5.5 - Beef, white flour, pork, lamb, dough and cakes made from white flour, fried food, all sugars, cigarettes (factory), yeast, refined salt and iodized salt, white rice, cottonseed oil, vinegar (all but apple cider vinegar).
pH 5.0 – Artificial sweeteners
pH 4.0 – Wine, spirits, coffee
pH 2.5 - Beer
pH 2.0 – Cocoa, various non-alcoholic carbonated and non-carbonated drinks, coca cola, all medicines, synthetic psychedelic drugs, pesticides, herbicides...
 It's interesting, yes thermal processing of alkalizing foods, let's say fruits and vegetables, they become acidifying if they are overcooked and prepared with oil. According to researches of Hay, Shelton and others, the constant intake of large amounts of acidifying foods burdens the organism and is most often the cause of disorders and the appearance of diseases. Their recommendation is that most (80%) foods should be alkalizing, and only 20% should be acidifying. In these 20% acidifying foods, it is best to use mildly acidic foods in their raw form such as grains, some legumes, seeds and nuts.
It's interesting, yes thermal processing of alkalizing foods, let's say fruits and vegetables, they become acidifying if they are overcooked and prepared with oil. According to researches of Hay, Shelton and others, the constant intake of large amounts of acidifying foods burdens the organism and is most often the cause of disorders and the appearance of diseases. Their recommendation is that most (80%) foods should be alkalizing, and only 20% should be acidifying. In these 20% acidifying foods, it is best to use mildly acidic foods in their raw form such as grains, some legumes, seeds and nuts.
 Tips for acid-base balance:
Tips for acid-base balance:
* chew food at least 35 times, because saliva adds a basic quality to each bite
* green leafy vegetables should be added to every meal
* devote 25 minutes to breathing exercises every day, as this improves the pH balance
* moderate exercises enhance detoxification and elimination of acidic substances from the body.
The role of calcium in maintaining optimal blood pH
 Calcium is one of the most important minerals for creating alkalinity. The human body contains as much as 2% of calcium or an average of 1.2 kg. This mineral has a positive effect on numerous body functions precisely because it perfectly regulates the acid-base balance in all body fluids. Blood is the most important in establishing this balance, and that is why the body makes sure that the blood has a pH value of 7.4, even at the expense of other body fluids. If the blood had a pH of 6.0, it would be acidic, we would not have enough oxygen and death would occur. That is why the body defends itself in such a way that it draws calcium from the bones and thus regulates its own pH value. And this is precisely the cause of many diseases.
Calcium is one of the most important minerals for creating alkalinity. The human body contains as much as 2% of calcium or an average of 1.2 kg. This mineral has a positive effect on numerous body functions precisely because it perfectly regulates the acid-base balance in all body fluids. Blood is the most important in establishing this balance, and that is why the body makes sure that the blood has a pH value of 7.4, even at the expense of other body fluids. If the blood had a pH of 6.0, it would be acidic, we would not have enough oxygen and death would occur. That is why the body defends itself in such a way that it draws calcium from the bones and thus regulates its own pH value. And this is precisely the cause of many diseases.
"All so-called natural deaths are nothing but the terminal point of saturation of the body with acidity", - George W. Crile of Cleveland, one of the most recognized surgeons in the world.
"It's not the countless names of diseases that matter, but the fact that they all stem from the root cause: too much acidity in the body." – Dr. Theodore A. Baroody, book "Alcalize or Die":
"Increased acidity of the body is the cause of all degenerative diseases. If there is a disturbance in the balance and the body begins to store acidity and toxins to a greater extent than it can excrete, then diseases appear." – Dr. Robert O. Young.

